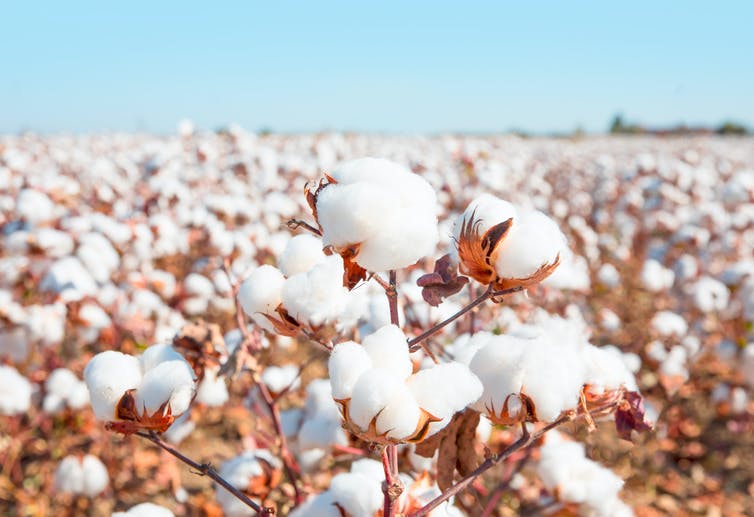
Introduction
Cotton is one of the most important fiber and cash crops of India and plays a dominant role in the industrial and agricultural economy of the country. In India, there are ten major cotton growing states which are divided into three zones, viz. north zone, central zone and south zone.
Cultivated Species & Varieties
There are four cultivated species of cotton viz. Gossypium arboreum, G.herbaceum, G.hirsutum and G.barbadense
Indore1, indore 2, Narmada A51, Badanwar 1, Khandwa1 , khandwa 2 Virkam, Ankur 3028, ankur 3244, Rasi 659, Ambuja, Moneymaker, rasi 773, Rasi 776, Ankur 555, Bayer 7172, Bayer 7272, US 51, US 71, US 81, US 91, Nuzeevidu 9013, Nuzeevidu balwan, Nuzeevidu Raghav, Sriram 6588, Goldi 333, Rasi 602, Rasi 650
Seed rate and spacing of cotton
Desi Varieties
Seed Rate : 15 to 22 kg / ha
Spacing: 75*15 cm, 60*30 cm,75*30 cm
BT Hybrid:
Seed Rate : 1.5 kg/ha
Spacing: 90*60 cm, 120*40, 120*60
spacing differs depending on the growth habit of a particular hybrid.
Climate & Soil Requirement
Cotton grown in tropical & subtropical conditions. A minimum temperature of 15oC is required for better germination at field conditions. The optimum temperature for vegetative growth is 21-27oC & it can tolerate temperature to the extent of 43oC but temperature below 21oC is detrimental to the crop.
Cotton is grown on a variety of soils ranging from well drained deep alluvial soils in the north to black clayey soils of varying depth in the central region and in black and mixed black and red soils in the south zone.
Method of sowing
Cotton is sown using tractor or bullock drawn seed drill or by dibbling. Hand dibbling of seeds at recommended spacing is commonly practiced in rainfed areas particularly for hybrids.
Fertilizer doses and method of application recommended for cotton crop in different zones
| Cultural Practices | Northern cotton zone | Northern cotton zone | Southern cotton zone |
| Fertilizers | N – 60 – 100 kg / ha. P and K dose as per soil test. No P need be applied if previous wheat received recommended P. 5.5 kg.Zn / ha. as ZnSo4 once in two cotton – wheat cycles | N – 60 – 100 kg / ha. P and K dose as per soil test. No P need be applied if previous wheat received recommended P. 5.5 kg.Zn / ha. as ZnSo4 once in two cotton – wheat cycles | N : P : K 40 – 20 – 20,60 – 30 – 30, 90 – 45 – 45 for varieties 100 – 50 – 50, 120 – 60 – 60, 150 – 60 – 60 for hybrids |
| Method of fertilizer application | i) Half N at thinning and remaining at first flowering; ii) Half N at sowing time in late sown crop; iii) Foliar application of N if needed; P to be drilled at sowing. | N in three splits at sowing, squaring and peak flowering stages. ( P & K according to soil test). Application of 2 % urea or DAP at flowering and early boll development. | N at squaring and peak flowering, P & K at sowing. In Karnataka entire NPK at planting ( rain fed cotton ), Half N and entire P & K at planting, remaining N at flowering (irrigated cotton ) N in 4 splits in irrigated hybrid cotton. |
Diseases of Cotton
1 ) Fusarium Wilt
Symptom: Initial symptoms on young seedlings are yellowing and browning of cotyledons, followed by brown ring on the petiole.Finally wilting & drying of the seedling occurs. Symptoms at later stages include loss of turgidity, yellowing, drooping and wilting starting from older leaves.Browning or blackening of vascular tissues occur on the stem and spreads upwards and downwards. Infected plants appear stunted with fewer bolls.
Management
Treat the acid-delinted seeds with Carboxin or Carbendazim at 4 g/kg.
Remove and burn the infected plant debris in the soil after deep summer ploughing during June-July.
Apply increased doses of potash with a balanced dose of nitrogenous and phosphatic fertilizers.
Apply heavy doses of farm yard manure or other organic manures at 100t/ha.
Spot drench with 0.05 % Benomyl or 0.1 % Carbendazim.
2 ) Root rot
Symptom
Germinating seedling shows black lesions on hypocotyls, girdling of stem and death of seedlings.
Affected basal stem becomes dark with bark shredding and scloretial bodies in the shredded bark.
The entire root system gets rotted, plants dried & can be easily pulled out.
Management
Treat the seeds with Trichoderma viride @ 4g/kg or Pseudomonas fluorescens
@ 10g/kg of seed.
Treat the seeds with Carboxin or Thiram at 5 g or Carbendazim at 2g/kg.
Spot drench with 0.1% Carbendazim or 0.05% Benomyl.
Apply farm yard manure at 10t/ha or neem cake at 2.5t/ha.
Adjust the sowing time, early sowing (First week of April) or late sowing (Last week of June) so that crop escapes the high soil temperature conditions.
3) Grey or Areolate mildew : Ramularia areola
| SymptomIrregular to angular pale translucent lesions on lower surface, bound by veinlets and grey powdery growth light green specks on upper surfaceIn severe cases whitish grey powdery growth on upper surface. Affected leaves dry up inward, turn yellow and fall prematurelyGrowing resistant varieties like Sujatha and Varalakshmi. ManagementRemove and burn the infected crop residues.Rogue out the self-sown cotton plants during summer months.Avoid excessive application of nitrogenous fertilizers/manures.Adopt the correct spacing based on soil conditions and varieties.Spray the crop with Carbendazim at 250-375g or wettable sulphur at 1.25-2.0 kg/ha, repeat after a week |
Adopt intercropping with sorghum or moth bean (Phaseolus aconitifolius) to lower the soil temperature.
Management : Treat the delinted seeds with Carbendazim or Carboxin@2g/kg or Thiram or Captan at 4g/kg.
4) Bacterial blight: Xanthomonas campestris p.v malvacearum
| Symptom: Water soaked, circular or irregular lesions on cotyledons which spread to petiole and stem and finally withering and death of seedling known as Seedling blightSmall, dark green, water soaked areas develop on lower surface of leaves, enlarge gradually and become angular when restricted by veins and veinlets and spots are visible on both the surface of leaves (Angular leaf spot)The infection of veins and veinlets shows blackening with crinkled and twisted leaves and bacterial oozing (vein necrosis or vein blighting)Black lesions on stem and branches, premature drooping off of the leaves resulting in die back known as Black armIt also affects the balls causing boll rot Management: Delint the cotton seeds with concentrated sulphuric acid at 100ml/kg of seed.Treat the acid delinted seeds with Carboxin or Oxycarboxin at 2 g/kg or soak the seeds in 1000 ppm Streptomycin sulphate overnight.Remove and destroy the infected plant debris.Rogue out the volunteer cotton plants and weed hosts. |
Pest of Cotton
1.Fruit borer: Helicoverpa armigera
Symptoms of damage
Bolls showing regular, circular bore holes
Larvae seen feeding on the boll by thrusting their heads alone inside and leaving the rest of the body outside
Presence of granular faecal pellets outside the bore hole.
A single larva can damage 30-40 bolls.
Management
Acephate 75%SP 780 g/ha
Azadirachtin 0.03% EC 500 ml/ha Carbaryl
10%DP 25 kg/ha Chlorantraniliprole 18.5%
SC 150 ml/ha Chlorpyriphos 20% EC 1250
ml/ha Diflubenzuron 25%WP 300 g/ha
Emamectin benzoate 5% SG 190-220 g/ha
2.Pink Bollworm: Pectinophora gossypiella
Symptoms of damage
Rosetted flowers
The holes of entry are plugged by excreta of larvae which are feeding inside the seed kernels.
They cut window holes (interlocular burrowing) in the two adjoining seeds thereby forming “double seeds”
The attacked buds and immature bolls drop off.
Discolored lint and burrowed seeds.
Management
Spraying any one of the following insecticides:
Phosalone 35%EC 2000 ml/ha
Triazophos 40EC 2.5l/ha
3.Spotted bollworms: Earias vittella, Spiny bollworm: Earias insulana
Symptom of damage
Drying and drooping of terminal shoots during pre –flowering stage
Shedding of squares and young bolls
Flaring up of bracts during square and young boll formation stage
Holes on bolls and rotting of bolls.
Management
Spraying any one of the following insecticides
Carbaryl 5%DP 20 kg/ha
Chlorantraniliprole 18.5% SC 150 ml/ha
Flubendiamide 39.35%SC 100-125 ml/ha
4.Leaf roller: Sylepta derogata
Symptom of damage
Leaves rolled in the form of trumpets fastened by silken threads
Marginal portion of leaves eaten away
Plants defoliated in severe attack
Management
Collection and destruction of shaded plant parts.
Hand picking and destruction of grown up caterpillars.
Spray any one of the following insecticides
chlorpyriphos 20 EC 2.0 l/ha
dichlorvos 76 WSC 1 lit/ha
fenitrothion 50 EC @ 625 ml.
5.Tobacco Cutworm: Spodoptera litura
Symptoms of damage
Scrapping the epidermal layer, leaving the skeleton of veins of leaf
During severe attack, only the stem and side shoots will be standing in the field without any leaf or bolls
Larvae feed the leaves by making small holes.
Management
Use of light traps to monitor and kill the attracted adult moths.
Set up the sex pheromone trap at 12/ha to monitor the activity of the pest and to synchronise the pesticide
application, if need be, at the maximum activity stage.
Spray any one of the following insecticides per ha using, a high volume sprayer covering the foliage and soil surface :
Chlorpyriphos 20 EC 2.0 l
Chlorpyriphos 20 EC 1.25 l
Chlorantraniliprole 18.5% SC 150 ml
Diflubenzuron 25%WP 300-350 g.
6.Leafhopper: Amrasca (Biguttula biguttula) devastans
Symptoms of damage
Tender leaves become yellow.The margin of the leaves start curling downwards and reddening sets in.In the case of severe infestation, leaves get a bronze or brick red colour which is typical “hopper burn” symptom.The margin of the leaves get broken and crumble into pieces when crushed.The leaves dried up and are shed and the growth of the crop is retarded.
Management
Apply carbofuran 3%CG 25 kg/ha
Spray any one of the following insecticides
Imidacloprid 200 SL at 100 ml/ha
Phosphamidon 40 SL 600 ml/ha
Acetamiprid 20%SP 50 g/ha
Azadirachtin 0.03%WSP 500-1000 g/ha
Buprofezin 25% SC 1000 ml/ha
Clothianidin 50%WDG 30-40 kg/ha
Diafenthiuron 50%WP 600 g/ha
7.Cotton aphid: Aphis gossypii
Symptom of damage
Infesting tender shoots under the surface of the leaves.
Curling and crinkling of leaves
Stunted growth
Blighted appearance when infestation is severe
Development of black sooty mould due to the excretion of honey dew giving the plant a dark appearance
Management
Spray any one of the following insecticides (500 l spray fluid/ha)
Methyl demeton 25 EC 500ml/ha
Dimethoate 30 EC 500ml/ha
Acetamiprid 20%SP 50 g/ha
Azadirachtin 0.03% EC 500 ml/ha
Buprofezin 25% SC1000 ml/ha
Carbosulfan 25%DS 60g/kg seed
Chlorpyrifos 20% EC 1250 ml/ha
Diafenthiuron 50%WP 600 ml/ha
8.Thrips: Thrips tabaci
Symptom of damage
Shriveling of leaves due to scrapping of epidermis and desapping
Attacked terminal buds – have ragged edges
Silvery shine on the undersurface of leaves
Management
Seed treatment with imidacloprid 70 WS at 7 g/kg protects the crop from aphids, leafhoppers and thrips upto 8 weeks.
Spray any one of the following insecticides (500 l spray fluid/ha)
Methyl demeton 25 EC 500ml/ha
Dimethoate 30 EC 500ml/ha
Buprofezin 25% SC 1000 ml/ha
Diafenthiuron 50%WP 600 g/ha
Dimethoate 30%EC 660 ml/ha
Fipronil 5%SC 1500-2000 ml/ha
9. Whitefly: Bemisia tabaci
Symptom of damage
Chlorotic spots on the leaves which latter coalesce forming irregular yellowing of leaf tissue which extends from veins to the outer edges of the leaves
Severe infestation results in premature defoliation
Development of sooty mould
Shedding of buds and bolls and poor boll opening
It also transmits the leaf curl virus diseases of cotton.
Management
Spray
Acetamiprid 20%SP 100 g/ha Azadirachtin 0.15% 500-1000 ml/ha, Buprofezin 25% SC
1000 ml/ha Chlorpyriphos 20% EC 1250 ml/ha Clothianidin 50%WDG 40-50 g/ha Diafenthiuron 50%WP 600g/ha Fipronil 5%SC 250-340 ml/ha Imidacloprid 17.8% SL100 -125 ml/ha
10.Red cotton bug: Dysdercus cingulatusi
Symptom of damage
Red stained lint and rotting bolls.Inner boll wall with warty growth or water soaked spots Young bolls abort and turn dark brown.The bacterium Nematospora gossypii enters the site of injury and stains the fibre.
Management
Plough the field to expose the eggs.
Spray phosphamidon 100 EC@250 ml/ha