Introduction
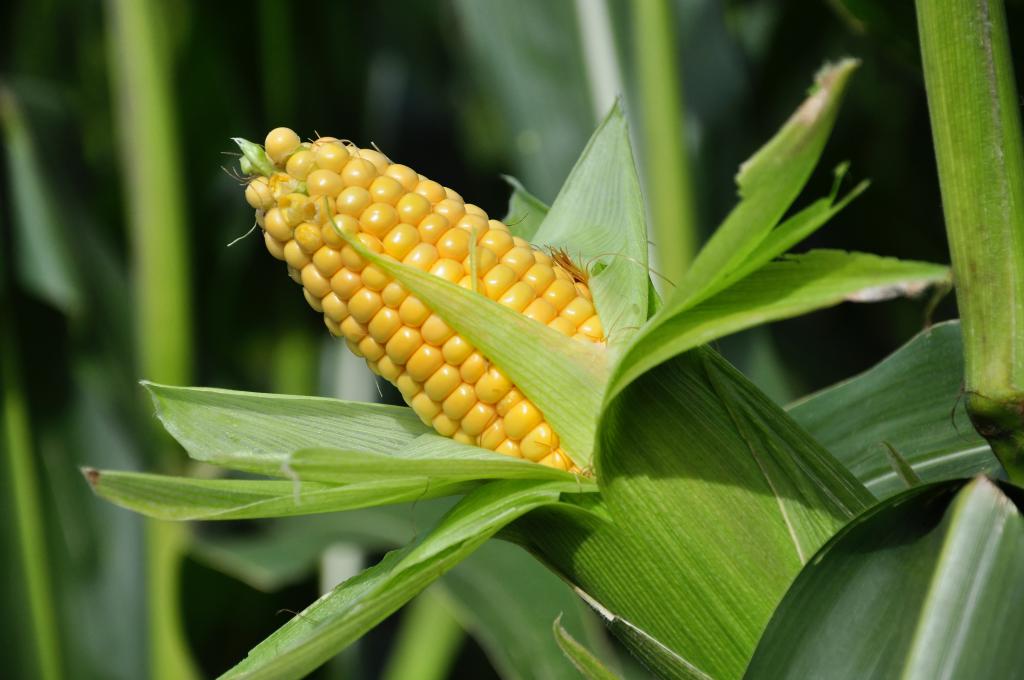
Maize is the world’s leading crop and is widely cultivated as cereal grain that was domesticated in central America. It is one of the most versatile emerging crops having wider adaptability, maize is known as queen of cereals because of its highest genetic yield potential.
Varieties
Ganga 5, Vivek maize hybrid 47, Vivek maize hybrid 53, Bio 9544, Dhawal, navjot, Shalimar sweetcorn, VL sweetcorn, Shiats, Maize VGIH.
Seed rate and spacing
Depending upon the seed size 18-22.5kg of seed per ha are required
Spacing: 60-20 cm 75-25 cm.
Climate & Soil Requirement
Any well-drained soil is suitable for maize. Sandy and sandy loam fertile soils are preferable. It requires a deep fine and firm tilth.
Method of sowing
Seeds should be dibbled at a depth of 3 -4 cm in rows 65-75 cm apart and at a distance of 20-25 cm from seed to seed within the rows. Two seeds per hill are to be sown followed by thinning10 days after germination retaining one seedling/ hill. Depending upon the fertility status of the soil, a wider spacing can be used. Varieties like Diara can be sown at clo spacing because of their short stature and shorter duration.
Fertilizer doses
| Nutrient | Requirement kg/ha | Form | Fertilizer requirement kg/ha |
| N | 60 | Urea | 134 |
| P2O5 | 40 | SSP | 250. |
| K2O | 40 | MOP | 9 |
Diseases of Maize
1. Downy mildew / Crazy top: Peranosclerospora sorghi
Symptoms: Chlorotic streaks appear on the leaf and white fungus growth is seen on both the surfaces of leaf. Affected plants become stunted and exhibit bushy appearance due to shortening of internodes. Sometimes leafy growths in the tassel and proliferation of axillary buds on the stalk of the tassel are noticed.
Management: Rogue out affected plants, Use resistant TNAU maize hybrid COH-6, Soil application of P. fluorescens (or) T. viride @ 2.5 kg / ha + 50 kg of well decomposed FYM (mix 10 days before application) or sand at 30 days after sowing. Spray Metalaxyl @ 1000g(or) Mancozeb 2g/lit at 20 days after sowing.
2.Leaf Blight: Exserohilum turcicum & Helminthosporium maydis
Turcicum Leaf Blight Symptoms: The fungus affects the crop at a young stage. Early symptoms are oval, water-soaked spots on leaves. Mature symptoms are characteristic cigar shaped lesions that are 3 to 15cm long. Lesions are elliptical and tan in color, developing distinct dark areas as they mature that are associated with fungal sporulation. Lesions typically first appear on lower leaves, spreading to upper leaves and the ear sheaths as the crop matures. Under severe infection, lesions may coalesce, blighting the entire leaf.
Maydis Leaf Blight Symptoms: Small yellowish round or oval spots appear on the leaves. These spots enlarge, become elliptical and the center becomes straw coloured with a reddish brown margin. Conidia and conidiophores are formed in the center.
Management
Rogue out affected plants.Resistant cultivers – Deccan, VL 42, Prabhat, KH-5901, PRO-324, PRO-339, ICI-701, F- 7013, F-7012, PEMH 1, PEMH 2, PEMH 3, Paras, Sartaj, Deccan 109, COH-6.Soil application of P. fluorescens (or) T. viride @ 2.5 kg / ha + 50 kg of well decomposed FYM (mix 10 days before application) or sand at 30 days after sowing
Spray Matalaxyl 1000 g / Mancozeb 2 g/liter at 10 days interval after first appearance of the disease.
3.Charcoal rot: Macrophomina phaseolina
Symptoms: The pathogen affects the plant mostly after flowering and the disease is named as Post Flowering Stalk Rot (PFSR).The stalk of the infected plants can be recognized by greyish streak.The pith becomes shredded and greyish black minute sclerotia develop on the vascular bundles. Shredding of the interior of the stalk often causes stalks to break in the region of the crown.The crown region of the infected plant becomes dark in colour.Shredding of root bark and disintegration of root system are the common features.
Management :Follow crop rotation,Avoidance of water stress at flowering time reduced disease incidence, Avoid nutrient stress.Apply potash @ 80 kg/ha in endemic areas, Soil application of P. fluorescens (or) T. viride @ 2.5 kg / ha + 50 kg of well decomposed FYM (mix 10 days before application) or sand at 30 days after sowing.
4.Corn rust: Puccinia sorghi
Symptoms:
On both the surfaces of the leaf, brown pustules are seen. These represent the uredosori of the fungus. The alternate host is Oxalis corniunlata. Cool temperature and high relative humidity favours the disease
Management:
Destroy alternate plant host, Soil application of P. fluorescens (or) T. viride @ 2.5 kg / ha + 50 kg of well decomposed FYM (mix 10 days before application) or sand at 30 days after sowing. Spray Mancozeb 1.25 kg/ha.
Pest of Maize
1.Stem borer: Chilo partellus
Symptoms
Central shoots withers and leads to “dead heart”. Larvae mines the midrib, enters the stem and feeds on the internal tissues. Bore holes visible on the stem near the nodes. Young larva crawls and feeds on tender folded leaves causing typical “shot hole” symptoms. Affected parts of stem may show internally tunnelling caterpillars
Management
Mix any of the following granular insecticides with sand to make up a total quantity of 50 kg and apply in the leaf whorls on the 20th day of sowing
Phorate 10% CG10 kg/ha
Carbaryl 4% G 20 kg/ha.
For stem borer, release egg p[arasitoid Trichogramma chilonis @2,50,000 /ha coinciding egg laying period. Three releases at weekly intervals are desirable. Third release is to be accompanied with larval parasitoid Cotesia flavipes @ 5000/ha
If granular insecticides are not used, spray any one of the following :
Carbaryl 50 WP 1 kg/ha on the 20th day of sowing (500 l of spray
fluid/ha). Dimethoate 30% EC 660 ml/ha
2.Pink stem borer: Sesamia inferens
Symptoms
Pink larva enters into the stem causing dead heart symptoms
Management
Spray phosaloneb 35%EC at every 20 days interval.
3.Corn worm/Earworm: Helicoverpa armigera
Symptom
Larva feeds on silk and developing grains.
Management
Set up of light traps
Set up sex pheromone traps at 12/ha
Two applications of NPV at 10 days interval at 1.5 X1012 POB along with Crude sugar 2.5 kg + cotton seed kernel powder 250 g on the ear heads.
4. Leafhopper: Pyrilla perpusilla
Symptom : Leaves become yellow
Covered with black sooty mould.
Top leaves get dried up and lateral buds germinate.
Management
Avoid excessive use of nitrogenous fertilizers, Set up light trap. Detrash: 150 and 210th DAP
Release lepidopteran parasitoid: Epiricrania melanoleuca @8000 -10,000 cocoon /ha (or) 8 – 10 lacs egg/ha.
Spray any one of the following on the 150th and 210th day (1000 l spray fluid) Malathion 50 EC 2000 ml Monocrotophos 36 WSC 2000 ml