Introduction
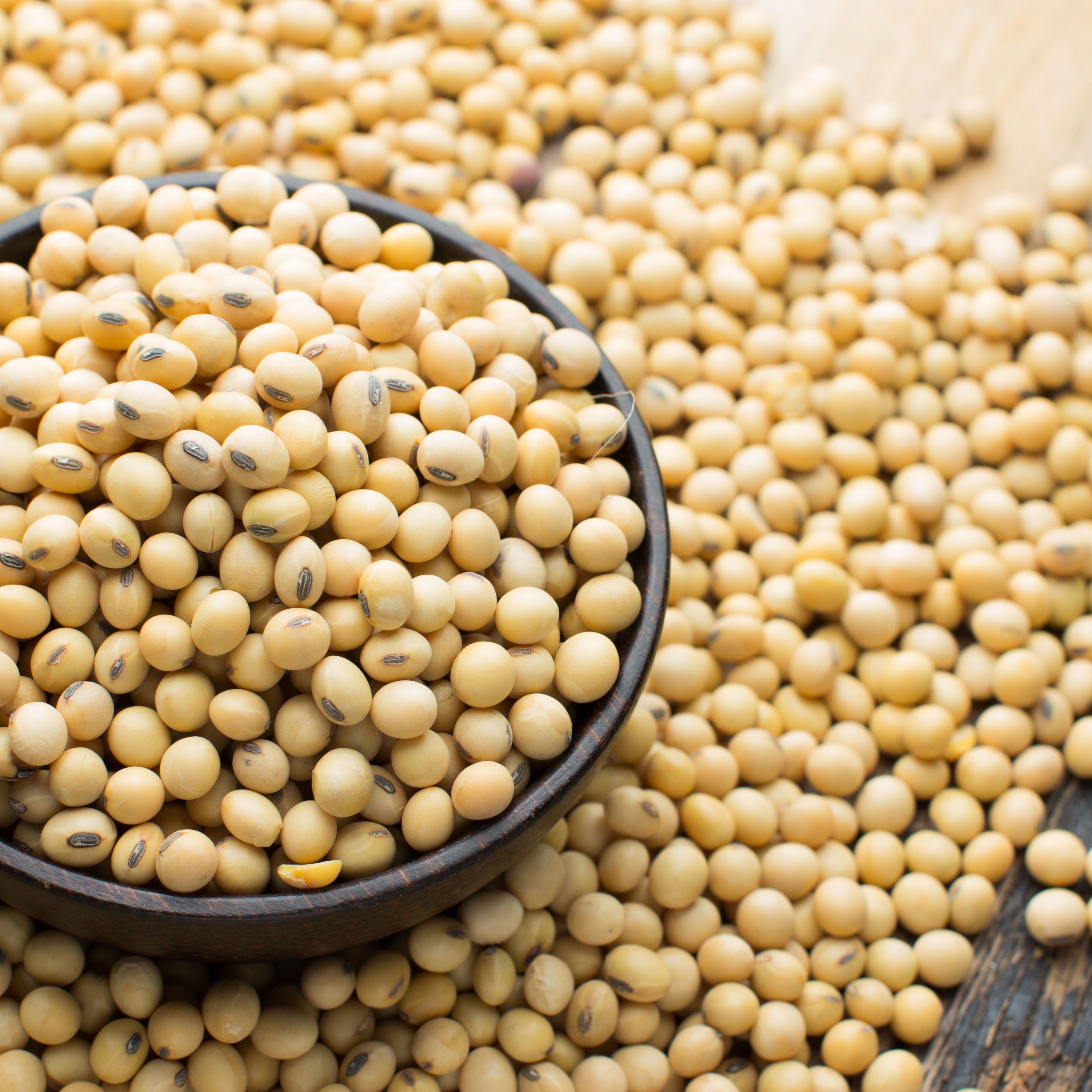
Soybean, (Glycine max), also called soja bean or soya bean, annual legume of the pea family (Fabaceae) and its edible seed. The soybean is economically the most important bean in the world, providing vegetable protein for millions of people and ingredients for hundreds of chemical products..
Varieties
Bragg,JS2, Ankur, DS 73-16, PK327, PK271, PK308, Moti, JS97-52, JS335, JS 2098, Raj Soya-24 (RVS 2002-4), CO (SOY)-3, Dsb-1, JS 95-60, JS 97-52, JS-2029, JS-2034, MAUS-158, NRC-86 (Ahilya), Palam soya (30-1-1), Pant Soya-2 (RKS-18), Pant Soybean 1225 (PS-1225), Pant Soybean-1347 (PS-1347), Phule Kalyani (DS-228), Pratap Soya-45 (RKS-45), PRS-1, PUSA 97-12 (DS-9712), Pusa 98-14, RAUS-5 (Pratap soya-1), RKS-24, SL-525, SL-688, TAMS-38, TAMS-9821, VL Soya-59, VL Soya-63, VL Soya-65
Seed rate and spacing
Seed rate: 50 to 60kg / ha
Spacing: 10*45 cm
Climate & Soil Requirement
Soybean can be grown on wide range of soils but it grows best on fertile well drained loamy soils. Water logging is injurious to the crop. In acidic soils where pH is below 6.0, lime (200 mesh powder form) should be added @ 2 t/ha, atleast 7days before sowing. L is necessary once in three years.
Method of sowing
Soybean is sown using tractor or bullock drawn seed drill.
Fertilizer doses
| Nutrient | Requirement (kg/ha) | Form | Fertilizer requirement Kg/ Ha |
| N | 20 | Urea | 45 |
| P2O5 | 60 | SSP | 375 |
| K2o | 40 | MOP | 70 |
Pest of Soybean
1.Stem fly: Melanagromyza sojae
Nature of damage: After hatching from the egg yellowish maggots bore the nearest vein of the leaf. The maggot then reach the stem through petiole and bore down the stem.If the infected stem is opened by splitting, distinct zigzag reddish tunnel can be seen with maggot or pupae inside it. The maggots feed on cortical layers of the stem, may extend to tap root, killing of the plant.
Management Practices: Foliar spray: Ethion 50% EC@1500ml/ha in 500-1000 lit of water (600ml/acre in 200-400 lit of water) or Indoxacarb 15.8 % EC@333ml/ha in 500 lit of water (133ml/acre in 200 lit of water) or Thiamethoxam (12.6%) + Lambdacyhalothrin (9.5%) ZC@125ml/ha in 500 lit of water (50ml/acre in 200 lit of water) or Chlorantraniliprole 18.5% SC@150ml/ha in 500-750 litof water (60ml/acre in 200-300 lit of water) or Lambda-cyhalothrin 4.9% CS@300ml/ha in 500 lit of water (120ml/acre in 200 lit of water), Phorate 10 % CG @ 15 kg / ha. (6 kg/acre).
2.White fly:Bemisia tabaci
Nature of damage: The nymphs and adults suck sap from lower surface of tender leaves. Sooty mould developed on honeydew secretions interferes with the photosynthesis and results in poor growth of the plant. Due to attack of the insect the leaves turn yellow and become curled. The insect acts as a vector for yellow mosaic virus disease in soybean.
Management Practices:Use yellow sticky trap.Use recommended seed rate. Pupal parasitoids- Encarsia Formosa, Eretmocerus spp.
3.Girdle beetle:Obereopsis brevis
Nature of damage: Girdling of stems and petioles. The inside of the stem is eaten by the grub and a tunnel is formed inside the stem. The leaves of plant of infected portion are unable to get the nutrient and are dried up. In later stages the plant is cut at about 15 to 25 cm above the ground.The infected portion above the circular cut is unable to get any nutrition so it dries up.
Management Practices: Foliar spray: Chlorantraniliprole 18.5% SC@150ml/ha in 500-750 lit of water (60ml/acre in 200-300 lit of water) or Thiamethoxam (12.6%) + Lambdacyhalothrin (9.5%) ZC@ 125ml/ha in 500 lit of water (50ml/acre in 200 lit of water) or Thiacloprid 21.7% SC@750ml/ha in 500 lit of water) 300ml/acre in 200 lit of water) or Triazophos 40% EC@625ml/ha in 500 lit of water (250ml/acre in 200 lit of water) or Profenofos 50% EC@1000ml/ha in 500 lit of water (400ml/acre in200 lit of water) or Ethion 50% EC@1500ml/ha 500-1000 lit of water (600ml/acre in 200-400 lit of water)
4.Semi-looper:Thysanoplusia orichalcea
Nature of damage: The small larva feeds on lower side of leaves leaving translucent feeding windows. Late larval instars feed on leaves and make holes. In case of severe infestation, they defoliate the entire plant and leave only the stem.
Management Practices: Foliar spray:Thiamethoxam (12.6%) + Lambdacyhalothrin (9.5%) ZC@125ml/ha in 500 lit of water (50ml/acre in 200 lit of water) or Flubendiamide 39.35% M/M SC @150ml/ha in 500 lit of water (60ml/acre in 200 lit of water) or Indoxacarb 15.8 % EC@333ml/ha in 500 lit of water (133ml/acre in 200 lit of water) or Lambda-cyhalothrin 4.9% CS@300ml/ha in 500 lit of water (120ml/acre in 200 lit of water) or Chlorantraniliprole 18.5% SC@150ml/hain 500-750 lit of water (60ml/acre in 200-300 lit of water) or Profenofos 50% EC@1000ml/ha in 500 lit of water (400ml/acre in 200 lit of water)
5.Tobacco caterpillar: Spodoptera litura
Nature of damage: Larva feed on the chlorophyll of the leaves. The eaten leaves give the appearance of whitish yellow web.
Management Practices: Indoxacarb 15.8 % EC@333ml/ha in 500 lit of water (133ml/acre in 200 lit of water) or Spinetoram 11.7 % SC@450ml/ha in 500-625 lit of water (180ml/acre in 200-250 lit of water) or Flubendiamide 39.35% M/M SC@150ml/ha in 500 lit of water (60ml/acre in 200 lit of water)
6.Bihar hairy caterpillar:Spilosoma oblique
Nature of damage: The leaves of the plant give an appearance of net or web.
Management Practices : Deep summer ploughing. Avoid premonsoon sowing. Use optimum seed rate.Adequate plant spacing should be provided. Intercrop soybean either with (early maturing) pigeon pea variety or maize or sorghum in the sequence of 4:2 should be practiced.Collect & destroy infested plant parts, egg masses and young larva.Field Sanitation: Remove the infested plant parts at least once in 10 days and bury them in compost pit to monitor and reduce the population.Light Trap: Install one light trap (200W mercury vapour lamp) per hectare to catch the adults of some nocturnal pests such as hairy caterpillar (positively phototropic)
7.Pod borer: Helicoverpa armigera
Nature of damage: The young larva feeds on the chlorophyll of young leaves and skeletonize it.They feed voraciously on the foliage in early stage, may defoliate the plant and later they feed on flowers and pods.
Management Practices: Foliar spray: Flubendiamide 39.35% M/M SC@150ml/ha in 500 lit of water (60ml/acre in 200 lit of water)
Deep summer ploughingInstall pheromone traps at a distance of 50 m @ 5 traps/ha for each insect pest.Erect bird perches @ 50/ha.Clip terminal shoots on 100 days of crop growth.Setting of light traps (1 light trap/5 acre) to kill moth population.
Diseases of Soybean
1.Dry Root Rot / Charcoal Rot:Macrophomina phaseolina
Symptoms: The disease symptom starts initially with yellowing and drooping of the leaves. The leaves later fall off and the plant dies within a week. Dark brown lesions are seen on the stem at ground level and bark hows shredding symptom. The affected plants can be easily pulled out leaving dried, rotten root portions in the ground. The rotten tissues of stem and root contain a large number of black minute sclerotia.
Management Practices : Crop rotation with cereals, cotton or other non host crops for one or two years reduces the inoculums level in soil Maintain good crop vigour to reduce losses. In irrigated field, watering during periods of high temperature and drought stress.
Seed treatment with Carboxin 37.5 % + Thiram37.5 % DS @ 3 gm / kg seed.
2.Wilt: Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. tracheiphilum
Symptoms: Initially a few plants are noticed with pale green flaccid leaves which soon turn yellow. Growth is stunted, chlorosis, drooping, premature shedding or withering of leaves with veinal necrosis often occurs and finally plant dies within 5 days.Brownish, purple discoloration of the cortical area is seen, often extends throughout the plant.
Management Practices: Reducing soil compaction, delaying planting, crop rotation and seed treatments applied to high quality seed are good management practices for minimizing losses.
Seed treatment with Carboxin 37.5 % + Thiram37.5 % DS @ 3 gm / kg seed.
3.Yellow mosaic disease: Soybean Mosaic Virus
Symptoms: Diseased plants are usually stunted with distorted (puckered, crinkled, ruffled, narrow) leaves. Pods become fewer and smaller seeds. Infected seeds get mottled and deformed. Infected seeds fail to germinate or they produce diseased seedlings.
Management: Planting disease free seeds. However possible resistant variety should be grown to minimize the risk of disease appearance. Maintaining good weed control.
4.Rust:Phakopsora pachyrhizi.
Symptoms: Symptoms appear on all above ground parts of the plant. Large number of light brown pustules appears on lower surface of the leaves in the initial stages, later turns to reddish brown to tan colour.Uredial pustules become more numerous with advancing infection and often will coalesce forming larger pustules that break open releasing masses of uredospores.Lesions are generally restricted by veins giving angular appearance. In Kharif crop, the disease appears in the first week of September coinciding with flowering or pod formation. The leaves gradually become yellow and premature defoliation.
Management Practices: Spray with Hexaconazole 5% EC @ 100 ml / 100 liter of water.ORSpray with Kresoxim-methyl 44.3% SC @ 500 ml / ha in 500 lit of water (202 ml / acre in 202 liter of water).ORSpray with Propiconazole 25% EC 500 gm / ha in 500 liter of water (202 gm / acre in 202 liter of water).