Introduction
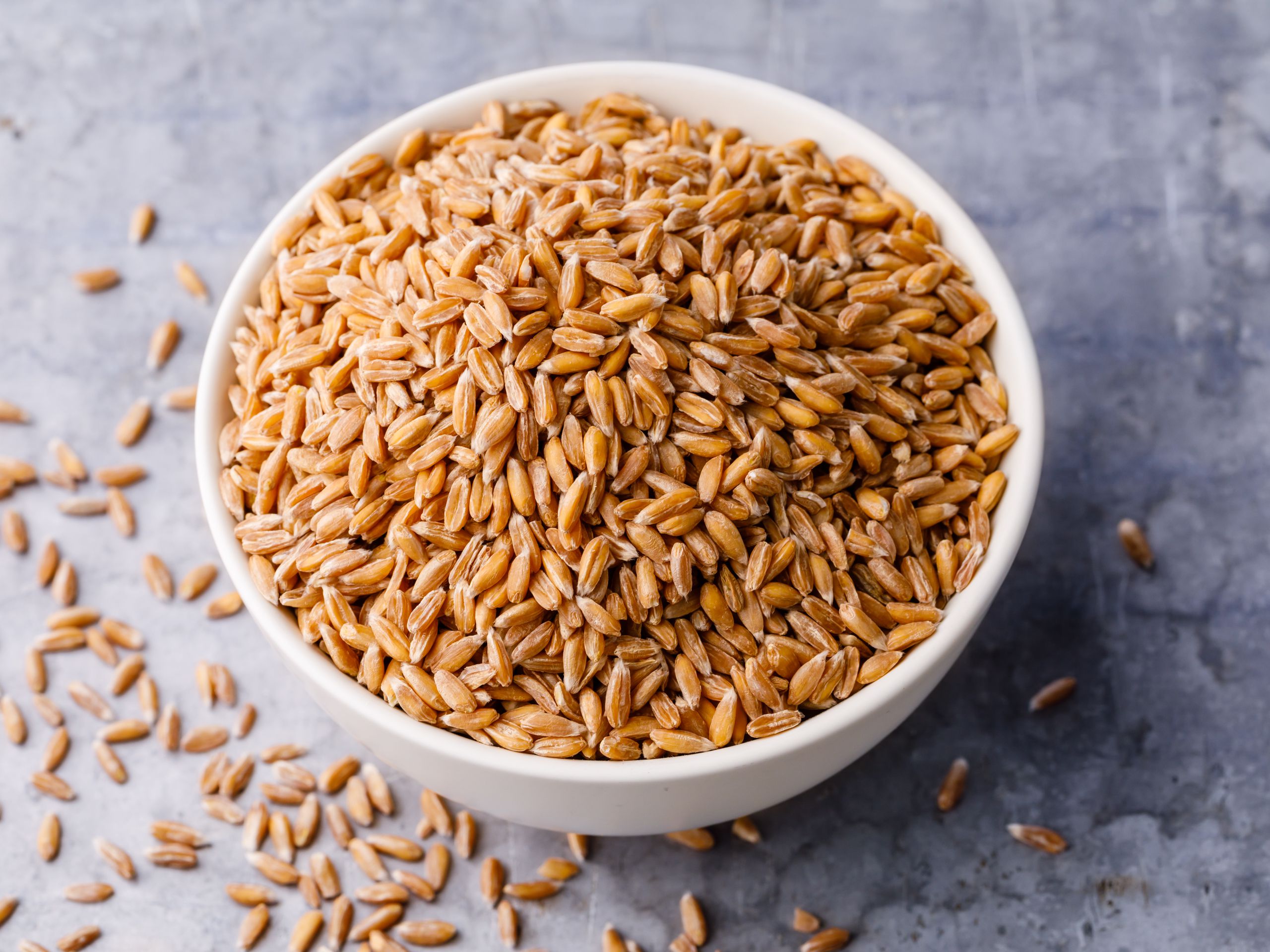
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus Triticum; the most widely grown is common wheat (T.aestivum). … Botanically, the wheat kernel is a type of fruit called a caryopsis.
Varieties
VL-832,VL-804, HS-365, HS-240 , HD2687,WH-147, WH-542, PBW-343, WH-896(d), PDW-233(d), UP-2338, PBW-502, Shresth (HD 2687), Aditya (HD 2781), HW-2044, HW-1085, NP-200(di), HW-741. C 306, Chhoti lerma, CPAN 1676 (Rohini), DBW 16, DBW 173, DBW 71, DBW 88, DBW 90, DL 153-2 (Kundan), DPW 621-50, DWR 17, GW 120, HD 1981 (Pratap), HD 2009 (Arjun), HD 2177, HD 2204, HD 2270, HD 2281, HD 2285 (Gobind), HD 2329, HD 2428, HD 2687 (Shresth), HD 2967, HD 3043, HD 3059, HD3086 (Pusa Gautami), HPBW 01, IWP 72, Kalyan sona, KSML 3, Lal Bahadur, PBW 154, PBW 175, PBW 226, PBW 299, PBW 373, PBW 396, PBW 502, PBW 550, PBW 590, PBW 644, PBW 65, PBW 660, PBW 725, PDW 215 (Duram), PDW 233 (Duram), PDW 291 (Duram), PDW 314 (Duram), RAJ 1482, RAJ 1972, RAJ 2184, RAJ 3077, RAJ 3765, RAJ 3777, RAJ 4120, RAJ 6560 (Durum), Safed Lerma, Sharbati sonora, Sonalika, Unnat PBW 343 (PBW 723), UP 2425, WB 2, WH 1021, WH 1080, WH 1105, WH 1124, WH 1142, WH 157, WH 283, WH 291, WH 711, WHD 896 (Duram), WHD 912 (Durum), WHD 943 (Duram), WL 2265, WL 410
Seed rate and spacing
100 kgs per hectare. Seeds should be sown at the depth of 5-6 cms in the soil in lines at a distance of 20- 22 cms from row to row.
Climate & Soil Requirement
August to September for higher region (above 800 MSL) as rainfed crop.
Last week of October to December for lower altitudes and plain areas under irrigated condition.
Selected well drained loamy soil with good irrigation prospect for growing of Wheat. Water logged areas should be avoided. The land should be ploughed thoroughly three to four times to make the soil well pulverized and should be leveled properly. Seeds should be sown when there is just sufficient moisture in the soil. If the soil is dry, a pre-sowing light irrigation should be given.
Method of sowing
Soybean is sown using a tractor or bullock drawn seed drill.
Fertilizer doses
| Sl no | Name of fertilizer | Irrigated | Un-irrigated |
| 1 | Urea | 175 Kgs (80 Kg. N) | 85 Kgs (40 Kg. N) |
| 2 | SSP | 250 Kgs (40 Kgs P2O5) | 125 Kgs (20 Kgs P2O5) |
| 3 | MOP | 65 Kgs (40 Kg. K2O) | 33 Kgs (20 Kg. K2O) |
Diseases of Wheat
1.Powdery Mildew: Erysiphe graminis
Symptoms: Powdery mildew can easily be diagnosed by the white, powdery patches that form on the upper surface of leaves and stem.Greyish white powdery growth appears on the leaf, sheath, stem and floral parts.Powdery growth later become black lesion and cause drying of leaves and other parts.
Management Practices: Foliar spray Triadimefon 25% WP @ 260-520 gm/ha in 750 liter of water (104-208 gm/acre in 300 liters of water).Azoxystrobin 18.2% w/w + Cyproconazole 7.3% w/w SC @ 500 ml/ha in 500 liters of water (400 gm/acre in 200 liters of water).Tebuconazole 50% + Trifloxystrobin 25% WG @ 300 gm/ha in 300 to 500 liters of water (120 gm/acre in 120 to 200 liters of water).Sulphur 80% WDG @ 2.5 kg/ha in 500 liters of water. (1 kg/acre in 200 liter water).Azoxystrobin 18.2% w/w + Difenoconazole 11.4% w/w SC @ 500 ml/ha in 500 liter water. (200 ml/acre in 200 liter water).
2.Leaf Blight: Alternaria triticina
Symptoms: Reddish brown oval spots appear on young seedlings with bright yellow margin. In severe cases, several spots coalesce to cause drying of leaves.
Management Practices: Foliar spray:Kresoxim-methyl 44.3% SC @ 500 ml/ha in 500 liter of water (200 ml/acre in 200 liter of water).Tebuconazole 38.39% w/w SC @ 600 ml/ha in 375 to 500 liters of water (240 ml/acre in 150 to 200 liters of water).Mancozeb 75% WP @ 1.5-2 kg/ha in 750 liter water. (600-800 gm/acre in 300 liter water).Zineb 75% WP @ 1.5-2 kg/ha in 750-1000 liter water. (600-800 gm/acre in 300-400 liter water)
3.Black Stem Rust: Puccinia graminis tritici
Symptoms: The first symptom of rust infection is flecking of leaves, leaf sheaths, culms and floral structures. These flecks soon develop as oblong, reddish brown uredo-pustules, frequently merging into one another, finally bursting to expose a mass of brown uredospores.When large number of uredosori burst and release their spores, the entire leaf blade and other affected parts will have a brownish appearance even from a distance. Later in the season, teleutosori are produced. On maturity the teleutosori burst open, exposing masses of dark brown teleutospores. In the transitional stage, there is a mosaic of brown and black masses of spores on the affected tissues, which dry up permanently.
Management Practices: Foliar spray:Mancozeb 75%WP @ 1.5 to 2 kg / ha in 750 liters of water (600 gm to 800 gm / acre in 300 liters of water).Propiconazole 25% EC @ 500 ml / ha in 750 liters of water (200ml / acre in 300 liters of water).Zineb 75 % WP @ 1.5-2kg/ha in 750 to 1000 liters of water (600-800 gm/acre in 300 to 400 liters of water).Azoxystrobin 18.2% w/w + Difenoconazole 11.4% w/w SC @ 500 ml/ha in 500 liter water. (200 ml/acre in 200 liter water)Spray Kresoxim-methyl 44.3% SC @ 500 ml / ha in 500 liters of water.Triadimefon 25% WP 750gm/ha in 750 liter of water. (300 gm/acre in 300 liter water)Azoxystrobin 18.2% w/w + Cyproconazole 7.3% w/w SC @ 500ml /ha in 500 liters water. (200 gm/acre in 200 liters water)
4.Brown Leaf Rust: Puccinia recondita
Symptoms:The most common site for symptoms is on upper leaf blades, however, sheaths, glumes and awns may occasionally become infected and exhibit symptoms.The pustules are circular or slightly elliptical, smaller than those of stem rust, usually do not coalesce.
Management Practices: Mancozeb 75%WP @ 1.5 to 2 kg / ha in 750 liters of water (600 gm to 800 gm / acre in 300 liters of water).
Propiconazole 25% EC 500 ml/ha in 750 liters of water (200ml/acre in 300 liters of waters).
Triadimefon 25% WP 1 kg/ha in 750 liters of water. (400 gm/acre in 300 liter water)
5.Yellow Strip Rust: Puccinia striformis
Symptoms: The uredosori appear as bright yellow pustules chiefly on the leaves.But in severe infections they may be seen on leaf sheaths also.The sori are elongated and are arranged in linear rows between the veins of the leaf and hence it is referred as Stripe Rust.
Management Practices:Propiconazole 25% EC @ 500 ml/ha in 750 liters of water (200 ml/acre in 300 liters of water).Picoxystrobin 7.05 % + Propiconazole 11.7 % SC @ 1000 ml / ha in 500 liter of water (400 ml / acre in 200 liter of water)Tebuconazole 25% WG @ 750 gm/ha in 500 liter water. (300 gm/acre in 200 liter water).Triadimefon 25% WP 1 kg/ha in 750 liters of water. (400 gm/acre in 300 liter water).Azoxystrobin 11% + Tebuconazole-18.3% SC W/W @ 750 ml/ha in 500 liter water. (300 ml/acre in 200 liter water.Tebuconazole 50% + Trifloxystrobin 25% WG @ 300 gm/ha in 300-500 liter water. (120 gm/acre in 120-200 liter water.
6.Loose Smut of Wheat:Ustilago nuda tritici
Symptoms: Infection is favored by cool, humid conditions during flowering period of the host plant.
Management Practices : Seed treatment: Carbendazim 50% WP @ 2 gm / kg seeds.Wet slurry treatment with Carbendazim 50% WP @ 1 liter / 10 kg seeds.Carboxin 75% WP @ 2-2.5 gm/kg seed.Tebuconazole 5.36% FS 3.33/10kg of seed Tebuconazole 5.4% w/w FS @ 3.0 ml/10 Kg of seed Carboxin 37.5% + Thiram 37.5% DS @ 3 gm / kg seed.Slurry treatment with Difenoconazole 3% WS @ 3gm/kg seed.Seed treatment with Carbendazim 25%+ Mancozeb 50% WS @ 30-35 g/kg of seed.Seed treatment with Carboxin 17.5% + Thiram 17.5% FF @ 25-30 gm/kg of seed.
7.Karnal Bunt:Neovossia indica
Symptoms:The infection is usually confined to a few grains in the spike with irregular arrangement.In some cases the infection may spread to only a part of the grains. In severe cases, the grain is reduced to black shiny sac of teliospores.As the grains mature the outer glumes spread and the inner glumes expand, exposing the bunted grains. The bunt balls are first enclosed by the pericarp but when it bursts the masses of bunt spores are exposed.The bunt affected plants emit a foul smell which is mainly due to the presence of Trimethyl amine.
Management Practices: Bitertanol 25% WP @ 2240 gm/ha in 750 liters of water (896 gm/acre in 300 liters if water).Propiconazole 25% EC @ 500 gm/ha in 750 liters of water (200 gm/acre in 300 liters of water).Seed Treatment with Carboxin 75 WP @ 2-2.5 gm/kg of seed. Propiconazole 25% EC 500 ml/ha in 750 liters of water (200 ml/are in 300 liters of water).Seed treatment with Thiram 75% WS @ 25-30 gm/kg of seed.Triadimefon 25% WP @ 500 gm/ha in 750 liters of water. (200 gm/acre in 300 liters of water)
Pest of Wheat
1.Termite: Odontotermes spp
Nature of damage: Workers feed on roots, stem of growing plants, even dead tissues of plant feeding on cellulose.The damaged plants dry up completely and are easily pulled out.Theplants damaged at later stages give rise to white ears.
Management Practices: Seed treatment:Thiamethoxam 30%FS @3.3ml/kg seed, Thiamethoxam 30%FS @175gm/kg seed, Chlorpyriphos 20% EC3-4ml/kg seed, Imidacloprid 18.5% + Hexaconazole 1.5% FS 2g/kg seed.Soil application:Fipronil 0.3% GR @20 kg/ha (8kg/acre),Foliar application:Chlorpyriphos 20% EC 2-3 lit/ha and 1.6-2.4 lit/ha.
2.Aphid: Rhopalosiphum padi
Nature of damage: Like other aphids, the nymphs and adults suck the sap from plants, particularly from their ears.They appear on young leaves or ears in large numbers during the cold and cloudy weather.The damage is particularly severe in years of cloudy weather.A heavily manured, well-irrigated and succulent crop will harbour the pest for a longer period and suffer greater damage.
Management Practices: Seed treatment:Thiamethoxam 70% WG @ 1.75g/kg seed, Imidacloprid 18.5% + Hexaconazole 1.5% FS 2g/kg seed.Foliar spray:Quinalphos 25% EC @1000ml/ha in 500-1000 lit of water (400ml/acrein 200-400 lit of water,Thiamethoxam 25% WG @ 50gm/ha in 500 lit water (20gm/acre in 200 lit water).
3.Army worm:Mythimna separata
Nature of damage: The primary symptom is defoliation of the plant. Larvae feed on leaves, chewing from the edges to the midrib, or on the heads of cereal plants.Heavy infestations can be very destructive; larvae may climb the plant and sever the neck just below the head.Some species may be found feeding at the soil surface, others underground feeding on roots, and still others feeding inside the stem.The armyworm feeds during dawn and dusk period as it is shy of sun light.
Management Practices: Foliar spray: Quinalphos 25% EC @1600ml/ha in 500-1000 lit of water (640ml/acre in 200-400 lit of water).
4.Brown mite: Petrobia lateens
Nature of damage: Nymph feed on leaves by sucking sap by inserting two needle like stylets into the leaf there by withdrawing nutrients from the plants.Affected leaves become whitish and under severe conditions become reddish brown and bronzy leaves wither and dry.
Management Practices: Foliar spray: Quinalphos 25% EC @1600ml/ha in 500-1000 lit of water (640ml/acre in 200-400 lit of water)
5.Pink stem borer: Sesamia inferens.
Nature of damage: Severe damage causes the stem to break. Severely infected plants due to stunting may appear to have sometimes the cob and tassel at one place. Whorl feeding of larvae results in rows of oblong holes in unfolding leaves unlike round shot holes produced by Chilo partellus. Later they bore in to central shoot resulting in the drying up of the growing point and formation of “dead heart” in young plant as a result of larval feeding sometimes the bottom internodes show circular ring like cuts. At ear head stage “white ears” are produced.
Management Practices: Collect the stubble’s after harvest and burn to destroy diapausing borers Set up light trap till midnight to attract and kill the stem borer moth. Bird perches @ 10/ acre should be erected for facilitating field visits of predatory birds.Parasitoids: Apanteles,Tetrastichus, Telenomus, Trichogramma japonicum ,T chilonis, Bracon etc.
Predators: Spiders, drynids, water bugs, mirid bugs, damsel flies, dragonflies, meadow grasshoppers, staphylinid beetles, carabids, coccinellids etc.